Carbon is a fundamental element that forms the backbone of organic life and is essential in various industries. Its forms, like graphite and diamonds, have diverse applications, but carbon emissions also play a significant role in environmental concerns like climate change.
What is Carbon?
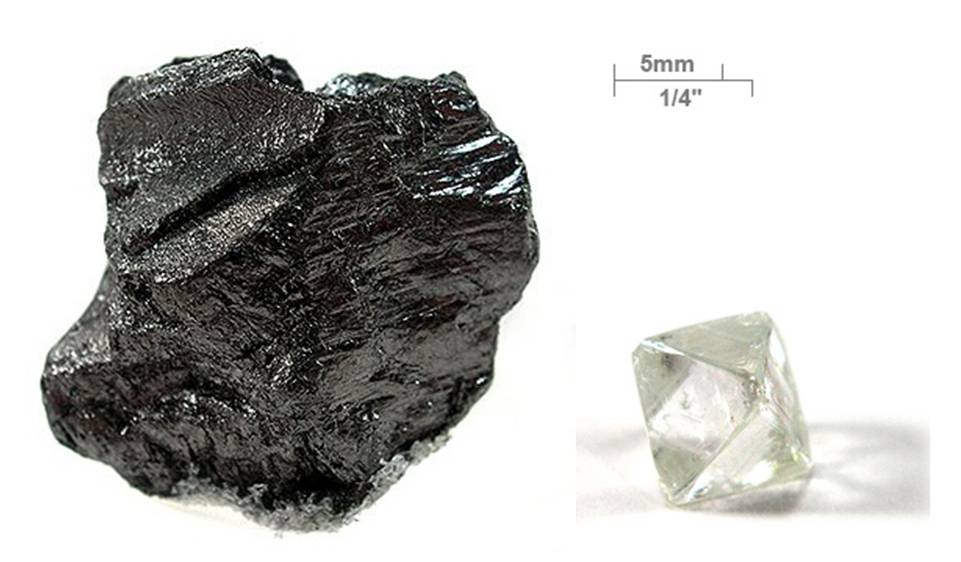

Carbon (C), the sixth element on the periodic table, is a fundamental building block of life and the backbone of organic chemistry. Found in all living organisms, it forms the basis of organic compounds and fuels our modern society, from fossil fuels to advanced materials like carbon fiber. Carbon’s versatility stems from its ability to form four covalent bonds, allowing it to create a vast array of structures, including simple molecules like carbon dioxide (CO2) and complex polymers.
Forms of Carbon:
Carbon exists in various forms, both naturally occurring and synthetic. The most well-known allotropes of carbon are:
- Diamond: The hardest naturally occurring material, used in industrial cutting tools and jewelry.
- Graphite: Used in pencils and as a lubricant, it is also a key material in batteries and advanced technology.
- Amorphous Carbon: Found in soot and coal, used in industrial applications and fuel production.
- Fullerenes and Nanotubes: Molecules made of carbon atoms shaped like spheres or tubes, important in nanotechnology. Each form of carbon has distinct physical properties that lend themselves to various industrial and technological applications.
Environmental Impact of Carbon:
Carbon’s role in the environment is both crucial and complex. It cycles through the earth’s ecosystems via processes like photosynthesis and respiration, making life possible. However, human activities such as burning fossil fuels have led to an excess of carbon in the atmosphere, primarily in the form of carbon dioxide (CO2).
This contributes to the greenhouse effect, leading to global warming and climate change. Managing carbon emissions and reducing our carbon footprint are critical challenges in the fight against environmental degradation.
Read More: Baddiehub.From – A Detailed Overview!
Industrial Uses of Carbon:
Carbon is indispensable to many industries. Some of the most prominent uses include:
- Energy: Fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas are carbon-based, powering industries and transportation.
- Metallurgy: Carbon is used in steel production (via carbonization processes) and in the creation of strong alloys.
- Chemical Industry: Carbon compounds are the basis for plastics, pharmaceuticals, and fertilizers.
- Construction: Carbon fiber and carbon-reinforced polymers are strong, lightweight materials used in aerospace, automotive, and construction industries.
Carbon in the Natural World:
In nature, carbon is part of the fundamental life cycle. Plants absorb CO2 during photosynthesis, releasing oxygen and storing carbon in their tissues. When plants and animals die, carbon returns to the soil, eventually becoming part of the fossil fuel reserves deep within the earth.
Oceans also act as major carbon sinks, absorbing large amounts of atmospheric CO2. However, the balance of carbon in nature is delicate and can be easily disrupted by human activities, leading to adverse environmental consequences.
Carbon in Modern Technology:
Carbon plays a vital role in modern technological advancements. Graphite is used in lithium-ion batteries, powering everything from smartphones to electric vehicles. Carbon-based materials like graphene, a one-atom-thick sheet of carbon atoms, have groundbreaking applications in electronics, offering high conductivity and strength. Additionally, carbon nanotubes are being explored for use in nanotechnology, medicine, and space exploration due to their unique properties.
The Economic Aspect of Carbon:
Carbon is central to the global economy, especially in the energy sector. Fossil fuels are the primary source of carbon emissions, power industries, and transportation. However, the economic implications of carbon extend beyond fossil fuels.
The carbon credit market, established to curb greenhouse gas emissions, allows companies to trade carbon allowances, incentivizing reduced emissions. Meanwhile, industries like carbon capture and storage (CCS) are emerging as key players in mitigating climate change, adding a new dimension to the carbon economy.
Carbon in Cultural and Historical Context:
Throughout history, carbon has played a significant role. In ancient times, charcoal, a form of carbon, was used in metallurgy for making tools and weapons. Diamonds, another form of carbon, have been symbols of wealth and power for centuries.
In the industrial age, the discovery of coal and oil transformed economies and societies, ushering in an era of unprecedented growth and development. Today, carbon remains at the heart of cultural, economic, and environmental discussions, especially in the context of sustainability and climate change.
Read More: Celebrate Your Graduation with an Unforgettable Fiji Adventure
Carbon-Based Materials and Applications:
The versatility of carbon allows it to be the foundation of numerous materials and applications, including:
- Carbon Fiber: A lightweight, high-strength material used in aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods.
- Carbon Composites: Used in construction and engineering for durable, lightweight structures.
- Carbon Nanotubes: Applied in electronics, nanotechnology, and medicine for their strength and conductivity.
- Graphene: Promising for use in flexible electronics, energy storage, and biomedicine due to its exceptional properties. These materials are revolutionizing industries by offering better performance, sustainability, and efficiency.
Industries and Carbon Management:

Industries around the world are focusing on carbon management to minimize their environmental impact. This includes reducing carbon emissions, adopting renewable energy sources, and improving energy efficiency.
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies are gaining traction, allowing industries to capture CO2 before it enters the atmosphere and store it underground. Additionally, carbon offsets and renewable energy certificates are helping companies reduce their carbon footprint while meeting regulatory and environmental standards.
Future Innovations in Carbon Use:
The future of carbon holds exciting possibilities. Innovations in carbon capture technology, such as direct air capture, aim to remove carbon directly from the atmosphere. Advances in carbon-neutral fuels, like biofuels and hydrogen, could significantly reduce our reliance on fossil fuels.
Carbon nanomaterials, including graphene and carbon nanotubes, are set to transform industries like electronics, medicine, and construction with their unique properties. As research continues, carbon-based innovations will play a critical role in addressing global challenges, particularly climate change and sustainable development.
FAQs:
1. What are the main forms of carbon?
Carbon exists in forms like diamond, graphite, amorphous carbon, fullerenes, and nanotubes, each with unique properties.
2. How does carbon impact the environment?
Carbon cycles naturally through ecosystems, but excess carbon dioxide (CO2) from human activities contributes to global warming and climate change.
3. What are the industrial uses of carbon?
Carbon is used in energy production (fossil fuels), steelmaking, chemical manufacturing, and construction materials like carbon fiber.
4. How is carbon used in modern technology?
Carbon-based materials such as graphene and carbon nanotubes are used in advanced electronics, batteries, and nanotechnology.
5. What are future innovations in carbon use?
Innovations include carbon capture technologies, carbon-neutral fuels, and carbon nanomaterials for applications in medicine, electronics, and sustainable energy.
Conclusion:
Carbon is a versatile element, integral to life, industry, and modern technology, with forms ranging from diamonds to advanced nanomaterials. While its uses drive economic growth, carbon emissions also contribute to environmental challenges like climate change. Future innovations in carbon capture and sustainable technologies will be key to addressing these global issues.
