animal:xbbivuxvusc= mouse refers to small mammals belonging to the rodent family, characterized by their round bodies, large ears, and long tails. They are among the most widespread mammals, thriving in diverse environments worldwide. Known for their keen senses and quick movements, mice are not only a vital part of food chains but also play an integral role in scientific research and ecological balance.
Habitat and Distribution:

Mice are highly adaptable, inhabiting regions ranging from forests and grasslands to urban areas. They can be found on almost every continent except Antarctica, thriving in conditions that provide shelter and food. Their ability to coexist with humans has allowed them to proliferate in cities and rural settings alike. These habitats vary based on the species, with some preferring burrows while others reside in crevices or constructed nests.
Mice in Research and Science:
Mice are pivotal in scientific research, acting as model organisms for studying genetics, diseases, and drug development. Their genetic similarity to humans, rapid reproduction, and ease of maintenance make them ideal for laboratory experiments. Breakthroughs in medicine, such as cancer treatments and genetic engineering, owe much to studies conducted on mice. Their role in advancing human health cannot be overstated.
Behavior and Diet:
Social Behavior:
Mice are social animals that communicate using sounds, scents, and body language. They form hierarchies within their groups, displaying complex social interactions. Grooming and nesting are shared activities that strengthen their bonds. Despite being social, mice exhibit territorial tendencies, particularly among males during the breeding season.
Also Read: Ceylan Eye Cream Reviews – Genuine Results from Real Users!
Feeding Habits:
Mice are omnivorous, feeding on grains, seeds, fruits, and small insects. They are opportunistic eaters and adapt their diet based on availability, often consuming human food when living near urban areas. Their constant gnawing is essential for maintaining their teeth, which grow continuously. Proper nutrition ensures their survival and reproductive success.
Why Are Mice Important in Research?
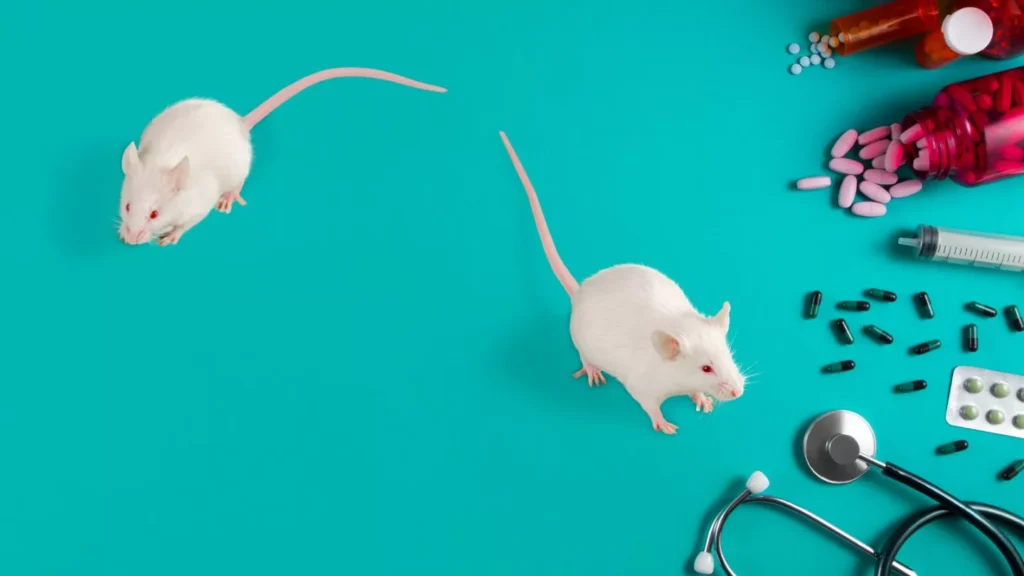
Mice have become indispensable in scientific research, serving as model organisms for numerous groundbreaking studies. Their unique biological characteristics and genetic similarity to humans make them ideal for exploring complex medical and biological questions. Below is an in-depth look at why mice are central to research efforts worldwide.
Genetic Compatibility with Humans:
Mice share approximately 98% of their genes with humans, making them highly effective for studying genetic disorders and human biology. Scientists can observe how specific genes function and interact, providing insights into diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and neurological disorders. Their genetic similarity allows researchers to replicate human conditions in controlled environments, ensuring accurate and reliable results.
Short Lifespan and Rapid Reproduction:
The short lifespan and rapid reproductive cycles of mice make them ideal for studying generational effects and the progression of diseases. Their ability to produce large litters within a short time enables researchers to conduct experiments on multiple subjects, enhancing the reliability of data. This characteristic also allows scientists to observe the long-term effects of treatments or environmental changes in just a few years.
Also Read: Malia Manocherian – Exploring the World of Art and Culture!
Cost-Effectiveness and Ease of Maintenance:
Mice are relatively inexpensive to house, feed, and care for compared to larger animals. Their small size requires less space, and their simple dietary needs reduce costs further. Additionally, their resilience and adaptability make them easy to maintain under controlled laboratory conditions, ensuring consistency in research.
Advancing Medical Treatments:
Mice have played a pivotal role in developing treatments for various human diseases. Breakthroughs in cancer therapies, vaccines, and genetic engineering have all relied on mouse models. For example, the creation of “knockout mice,” where specific genes are disabled, has revolutionized our understanding of gene functions and disease mechanisms.
What Role Do Mice Play in Ecosystems?

Mice serve as a food source for many predators, including birds, reptiles, and mammals, making them a vital link in food chains. They aid in seed dispersion and soil aeration through their foraging and burrowing behaviors. Their presence supports ecological balance, highlighting their environmental importance.
How Do Mice Impact Human Life?
Mice influence human life both positively and negatively. While they are indispensable in scientific research, they can also be pests, causing damage to crops and stored goods. Their role as disease carriers has historical significance, as seen during plagues. Nevertheless, their contributions to medicine and ecological services outweigh the challenges they pose.
What Adaptations Make Mice Successful Survivors?
Mice possess remarkable adaptations, such as their acute sense of smell and hearing, which help them detect danger and locate food. Their small size and agility enable them to evade predators and access tight spaces. Their ability to reproduce quickly ensures their populations remain stable even in adverse conditions.
Also Read: Kingymab – Revolutionizes Your Workout Routine!
What Are Some Interesting Facts About Mice?
- A mouse’s teeth never stop growing, necessitating constant gnawing to keep them trimmed.
- Mice can communicate using ultrasonic sounds undetectable to human ears.
- They have excellent memories, remembering paths and routes for long periods.
- Despite their small size, mice can jump nearly 12 inches vertically.
- A female mouse can have up to 10 litters annually, with an average of 5–6 pups per litter.
FAQ’s
1. Why are mice important in research?
Mice share 98% of their genes with humans, making them essential for studying genetics and diseases.
2. What role do mice play in ecosystems?
Mice serve as prey, help disperse seeds, and support ecological balance through their burrowing and foraging.
3. How do mice impact human life?
Mice aid scientific progress but can also act as pests and carriers of diseases, affecting crops and goods.
4. What adaptations make mice successful survivors?
Their keen senses, agility, and rapid reproduction ensure survival in diverse and challenging environments.
5. What are some interesting facts about mice?
Mice have ever-growing teeth, communicate with ultrasonic sounds, and can jump nearly 12 inches high.
Conclusion
Mice are fascinating creatures that play crucial roles in ecosystems, scientific research, and human life. Their adaptability, genetic similarity to humans, and unique behaviors make them indispensable in advancing medical science and maintaining ecological balance. Despite their challenges as pests, their contributions far outweigh the negatives.
Related Post:
- Also Read: Why You Feel Tired: 7 Common Mistakes Australians Make During Workouts
- Also Read: Why Invest in an Australian-Made Leather Purse?
- Also Read: How ABN Registration Affects Your Business Contracts
