In the fast-paced, competitive landscape of modern business, companies are constantly seeking ways to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall performance.
One of the most effective strategies for achieving these goals is preventive maintenance. Preventive maintenance involves regular and systematic inspection, detection, and correction of incipient failures before they develop into major defects. It is a proactive approach designed to ensure that machinery, equipment, and infrastructure operate smoothly and efficiently.
This blog post will delve into the importance of preventive maintenance and why it is crucial for business success.
Understanding Preventive Maintenance
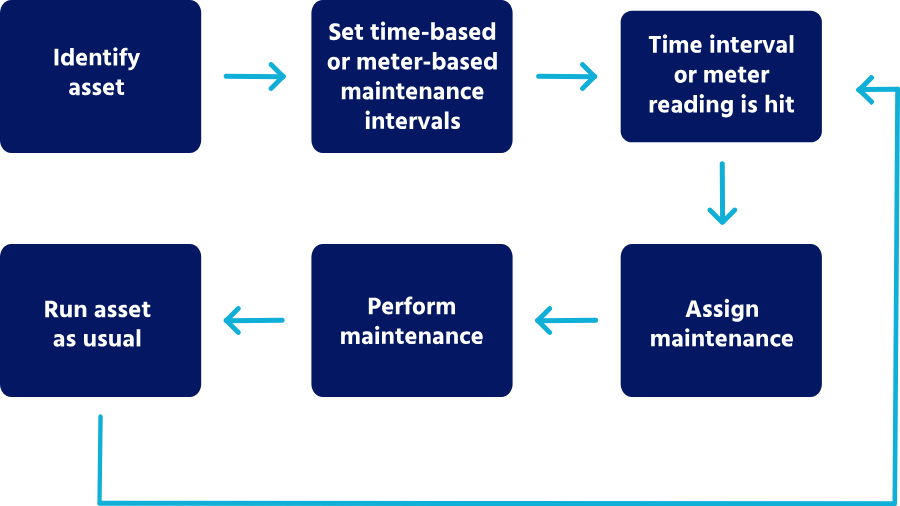
Preventive maintenance (PM) is a planned and controlled process that involves regular inspections, servicing, and maintenance of equipment to prevent unexpected failures and costly downtimes. It is different from reactive maintenance, where actions are taken only after equipment has failed. Instead, PM focuses on routine check-ups and timely interventions to maintain optimal operational conditions.
The key components of preventive maintenance include:
Scheduled Inspections: Regular checks to identify potential issues before they escalate.
Servicing and Repairs: Performing necessary repairs and replacements of worn-out parts.
Documentation and Monitoring: Keeping detailed records of maintenance activities and monitoring equipment performance over time.
Benefits of Preventive Maintenance
Reduced Downtime and Increased Productivity
Equipment failures can lead to significant downtimes, disrupting production schedules and leading to missed deadlines. Preventive maintenance helps identify and address issues before they result in equipment failure, thereby reducing unplanned downtimes. Consistent equipment performance ensures that production processes run smoothly, enhancing overall productivity.
Cost Savings
While preventive maintenance requires an upfront investment in time and resources, it ultimately saves money by avoiding the high costs associated with emergency repairs and equipment replacements. Regular maintenance helps extend the lifespan of machinery and reduces the likelihood of major breakdowns, which can be expensive to fix.
Improved Safety
Ensuring that equipment is in good working condition is essential for maintaining a safe work environment. Faulty machinery can pose significant safety risks to employees. Preventive maintenance helps identify and rectify potential hazards, reducing the risk of workplace accidents and injuries.
Enhanced Equipment Efficiency
Well-maintained equipment operates more efficiently, consuming less energy and reducing operational costs. Preventive maintenance ensures that machinery runs at optimal performance levels, leading to better energy efficiency and lower utility bills.
Better Compliance with Regulations
Many industries are subject to strict regulatory standards that mandate regular maintenance and safety checks. Preventive maintenance helps businesses comply with these regulations, avoiding potential fines and legal issues.
Prolonged Equipment Lifespan
Regular maintenance activities such as lubrication, cleaning, and part replacements help prolong the lifespan of equipment. This delays the need for costly capital investments in new machinery and ensures that existing assets are utilized to their fullest potential.
Implementing an Effective Preventive Maintenance Program
To reap the benefits of preventive maintenance, businesses must implement an effective PM program. Here are some key steps to consider:
Develop a Maintenance Schedule
Create a comprehensive maintenance schedule that outlines when and how often each piece of equipment should be inspected and serviced. This schedule should be based on the manufacturer’s recommendations, equipment usage patterns, and the criticality of each asset.
Utilize Maintenance Management Software
Implementing a computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) can streamline the planning, scheduling, and tracking of maintenance activities. A CMMS allows businesses to automate maintenance tasks, track work orders, and maintain detailed records of equipment history. The best part is that maintenance software free options are available on the Web, making it easier for businesses to get started.
Train and Equip Maintenance Personnel
Ensure that maintenance personnel are adequately trained and equipped to perform their tasks efficiently. Continuous training programs can help technicians stay updated with the latest maintenance techniques and safety protocols.
Conduct Regular Inspections and Audits
Regular inspections and audits help identify potential issues before they escalate. Conducting periodic audits of the maintenance program can also help identify areas for improvement and ensure that maintenance activities are being carried out as planned.
Monitor Equipment Performance
Implementing condition monitoring techniques such as vibration analysis, thermal imaging, and oil analysis can provide valuable insights into the health of equipment. Monitoring equipment performance helps detect early signs of wear and tear, enabling timely interventions.
Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Define and track KPIs to measure the effectiveness of the preventive maintenance program. Common KPIs include equipment uptime, mean time between failures (MTBF), and maintenance cost as a percentage of replacement asset value (RAV). Regularly reviewing these metrics can help identify trends and make informed decisions to optimize the maintenance strategy.
Overcoming Challenges in Preventive Maintenance
Implementing a preventive maintenance program can present several challenges, including:
Initial Costs and Resource Allocation
The initial costs of setting up a preventive maintenance program, including purchasing software, training personnel, and performing initial inspections, can be substantial. These upfront expenses can be a significant hurdle for many organizations, especially those with tight budgets.
However, these costs are outweighed by the long-term savings achieved through reduced downtimes and extended equipment lifespans. Investing in preventive maintenance can lead to fewer unexpected breakdowns, less overtime for emergency repairs, and a more stable production environment. Additionally, modern software solutions often offer scalable pricing models, making it easier for organizations of different sizes to implement such programs.
Resistance to Change
Employees may resist changes to established maintenance practices, especially if they are accustomed to a reactive approach. This resistance can stem from a lack of understanding of the new processes, fear of increased workload, or skepticism about the benefits of preventive maintenance.
Effective communication and training can help overcome this resistance by highlighting the benefits of preventive maintenance. Providing clear explanations, demonstrating successful case studies, and involving employees in the planning process can foster a sense of ownership and acceptance. Moreover, addressing concerns and providing continuous support can ease the transition and ensure the new practices are adopted smoothly.
Data Management
Managing and analyzing large volumes of maintenance data can be overwhelming. The sheer amount of data generated by modern equipment can lead to information overload, making it difficult to extract actionable insights. Implementing a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) can help streamline data management and provide valuable insights for decision-making.
A CMMS can automate data collection, organize maintenance schedules, and generate reports that highlight trends and potential issues. By leveraging the capabilities of a CMMS, organizations can make informed decisions, prioritize maintenance tasks effectively, and optimize resource allocation. Additionally, integrating CMMS with other enterprise systems can enhance overall operational efficiency and provide a comprehensive view of the maintenance landscape.
Balancing Maintenance and Production
Scheduling maintenance activities without disrupting production can be challenging. Maintenance needs to be performed regularly to prevent equipment failures, but halting production for maintenance can lead to significant downtime and lost revenue. Coordinating with production teams and planning maintenance during non-peak hours can help minimize disruptions.
Developing a detailed maintenance schedule that aligns with production timelines and incorporates flexibility for urgent repairs can ensure that both maintenance and production goals are met.
Furthermore, using predictive maintenance techniques, such as condition monitoring and trend analysis, can help identify the optimal times for maintenance, reducing the impact on production schedules. Employing a proactive approach and fostering collaboration between maintenance and production teams can lead to a harmonious balance, maximizing both uptime and equipment reliability.
The Bottom Line
Preventive maintenance is a critical component of business success, offering numerous benefits such as reduced downtime, cost savings, improved safety, enhanced equipment efficiency, better regulatory compliance, and prolonged equipment lifespan. By implementing an effective preventive maintenance program, businesses can ensure that their operations run smoothly and efficiently, ultimately leading to greater competitiveness and profitability.
In today’s dynamic business environment, the importance of preventive maintenance cannot be overstated. Companies that invest in preventive maintenance are better positioned to mitigate risks, optimize performance, and achieve long-term success. By adopting a proactive approach to maintenance, businesses can unlock significant value and ensure sustained growth and prosperity.